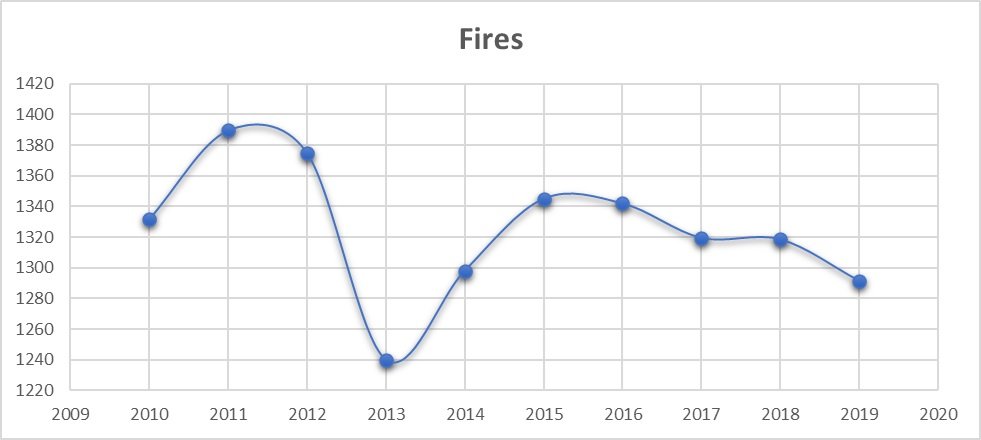
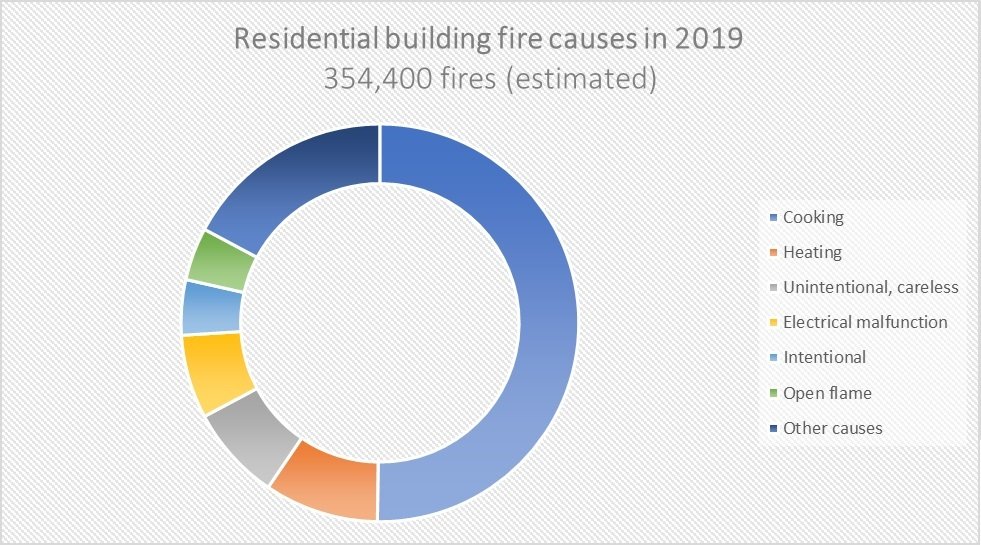
Recent posts


Research Paper Guides
by  Mary Watson
Mary Watson
 Mary Watson
Mary Watson